Mask Data Preparation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mask data preparation (MDP), also known as layout post processing, is the procedure of translating a file containing the intended set of polygons from an
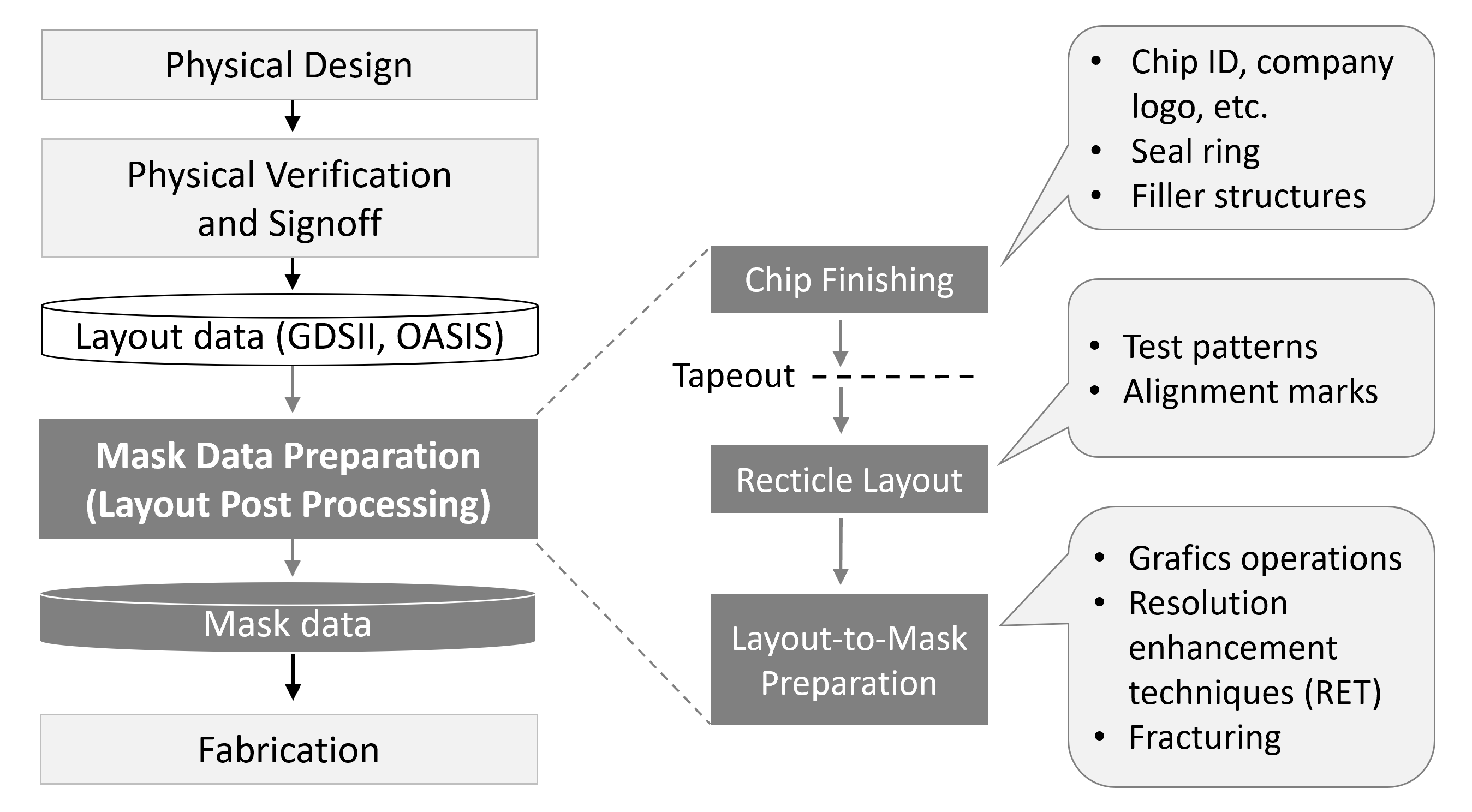 Although historically converting the physical layout into data for mask production was relatively simple, more recent MDP procedures require various procedures:
* ''Chip finishing'' which includes custom designations and structures to improve manufacturability of the layout. Examples of the latter are a seal ring and filler structures.
* Producing a ''reticle layout'' with test patterns and alignment marks.
* ''Layout-to-mask preparation'' that enhances layout data with graphics operations and adjusts the data to mask production devices. This step includes
Although historically converting the physical layout into data for mask production was relatively simple, more recent MDP procedures require various procedures:
* ''Chip finishing'' which includes custom designations and structures to improve manufacturability of the layout. Examples of the latter are a seal ring and filler structures.
* Producing a ''reticle layout'' with test patterns and alignment marks.
* ''Layout-to-mask preparation'' that enhances layout data with graphics operations and adjusts the data to mask production devices. This step includes
integrated circuit layout
Integrated circuit layout, also known IC layout, IC mask layout, or mask design, is the representation of an integrated circuit in terms of planar geometric shapes which correspond to the patterns of metal, oxide, or semiconductor layers that make ...
into set of instructions that a photomask
A photomask is an opaque plate with holes or transparencies that allow light to shine through in a defined pattern. They are commonly used in photolithography and the production of integrated circuits (ICs or "chips") in particular. Masks are used ...
writer can use to generate a physical mask. Typically, amendments and additions to the chip layout are performed in order to convert the physical layout into data for mask production.
Mask data preparation requires an input file which is in a GDSII
GDSII stream format (GDSII), is a binary database file format which is the de facto industry standard for Electronic Design Automation data exchange of integrated circuit or IC layout artwork. It is a binary file format representing planar geom ...
or OASIS format, and produces a file that is in a proprietary format specific to the mask writer.
MDP procedures
 Although historically converting the physical layout into data for mask production was relatively simple, more recent MDP procedures require various procedures:
* ''Chip finishing'' which includes custom designations and structures to improve manufacturability of the layout. Examples of the latter are a seal ring and filler structures.
* Producing a ''reticle layout'' with test patterns and alignment marks.
* ''Layout-to-mask preparation'' that enhances layout data with graphics operations and adjusts the data to mask production devices. This step includes
Although historically converting the physical layout into data for mask production was relatively simple, more recent MDP procedures require various procedures:
* ''Chip finishing'' which includes custom designations and structures to improve manufacturability of the layout. Examples of the latter are a seal ring and filler structures.
* Producing a ''reticle layout'' with test patterns and alignment marks.
* ''Layout-to-mask preparation'' that enhances layout data with graphics operations and adjusts the data to mask production devices. This step includes resolution enhancement technologies
Resolution(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
* Resolution (debate), the statement which is debated in policy debate
* Resolution (law), a written motion adopted by a deliberative body
* New Year's resolution, a commitment that an individual mak ...
(RET), such as optical proximity correction
Optical proximity correction (OPC) is a photolithography enhancement technique commonly used to compensate for image errors due to diffraction or process effects. The need for OPC is seen mainly in the making of semiconductor devices and is due to ...
(OPC) or inverse lithography technology (ILT).
Special considerations in each of these steps must also be made to mitigate the negative affects associated with the enormous amounts of data they can produce; too much data can sometimes become a problem for the mask writer to be able to create a mask in a reasonable amount of time.
Reticle layout
When a chip series is to be manufactured, the individual die is instantiated several times in the form of a matrix to produce what is termed the ''reticle layout''. This reticle layout consists of vertical and horizontal scribe lines that separate the individual dies that have been placed in a matrix format. The size of this matrix depends on the maximum exposable surface area based on the reticle size.Mask fracturing
MDP usually involves ''mask fracturing'' where complex polygons are translated into simpler shapes, often rectangles and trapezoids, that can be handled by the mask writing hardware. Because ''mask fracturing'' is such a common procedure within the whole MDP, the term fracture, used as a noun, is sometimes used inappropriately in place of the term ''mask data preparation''. The term fracture does however accurately describe that sub-procedure of MDP.References
Further reading
* A survey of the field, from which this summary was partly derived, with permission. * {{Cite book, author=Lienig, J., Scheible, J., title=Fundamentals of Layout Design for Electronic Circuits, url=https://www.ifte.de/books/pd/index.html, publisher=Springer, date=2020, doi=10.1007/978-3-030-39284-0, isbn=978-3-030-39284-0, s2cid=215840278 Chapter 3.3 covers mask data generation in detail. Electronic design automation